Food Defense for learners, QC, QA, Management, and all review team members protecting food & packaging from acts of intentional adulteration or tampering
Course Cost: POA
About Food Defense Training
Food Defense is the effort to protect food from acts of intentional adulteration or tampering. It is also referred to by the FAO as protecting food integrity and ensuring its authenticity.
Food Safe’s Food Defense Training:
- Reduces a company’s Food Defense risk the first time, proactively.
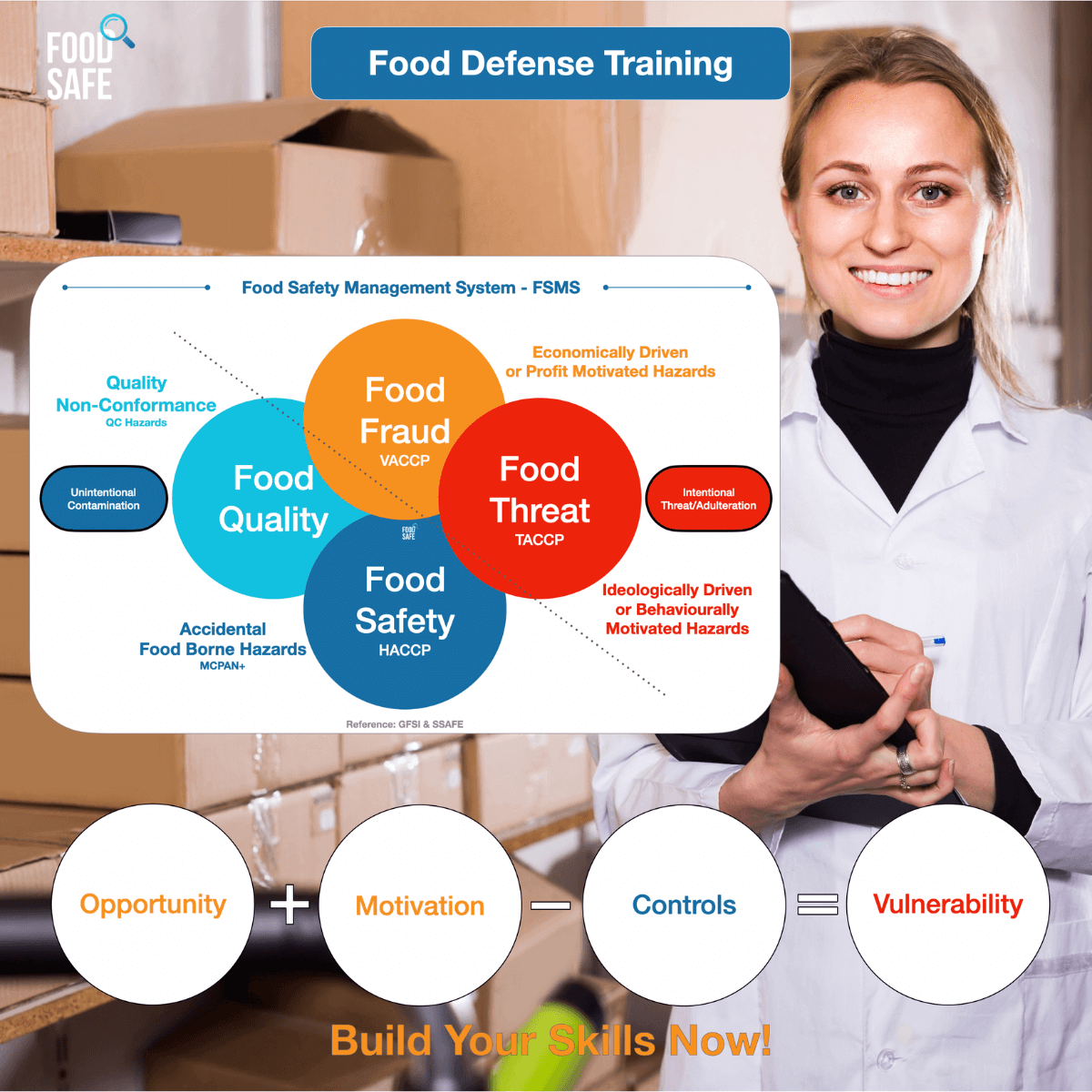
- Includes entire FSMS and VACCP & TACCP
- Covers Food Defense process steps, including Food Defense plan builder, template, and checklist
- Immediately meets audit requirements including BRCGS Issue 9, FDA, FSANZ, Codex FAO Food Security, GFSI, FSSC 22000 Version 6, SQF, and supplier requirements such as WSE Woolworths and McDonalds
- NZQA Training PTE Approved by MPI, all auditors and verifiers
- Provides a best-practice understanding, including all process steps for risk evaluation
- Ensures your team understands ‘why’ in an enjoyable and practical way!
This course is suitable for:
Operators, QC, QA, Quality officers, Management, Technical & all HACCP, VACCP & TACCP review team members
Useful for: Entire food supply chain, from farm to fork including production, support services & packaging companies
Course Duration: One-day course
Options: Expert instructor-led online and on-site

Course Content
- What is food defense, and why is it important?
- What is VACCP & TACCP and how this fits with HACCP under a Food Safety Management System (FSMS)
- Case study reviews of food safety threats and food vulnerabilities
- Examples of Biological and Chemical Terrorism directed at food, globally and in other countries such as the USA, New Zealand & Australia
- The UK Government Elliot Report
- Definitions and guidelines, such as PAS 96
- Regulatory and certification programs requirements including BRCGS, FDA, FSANZ, Codex FAO Food Security, GFSI, and FSSC 22000
- Food defense control measures include:
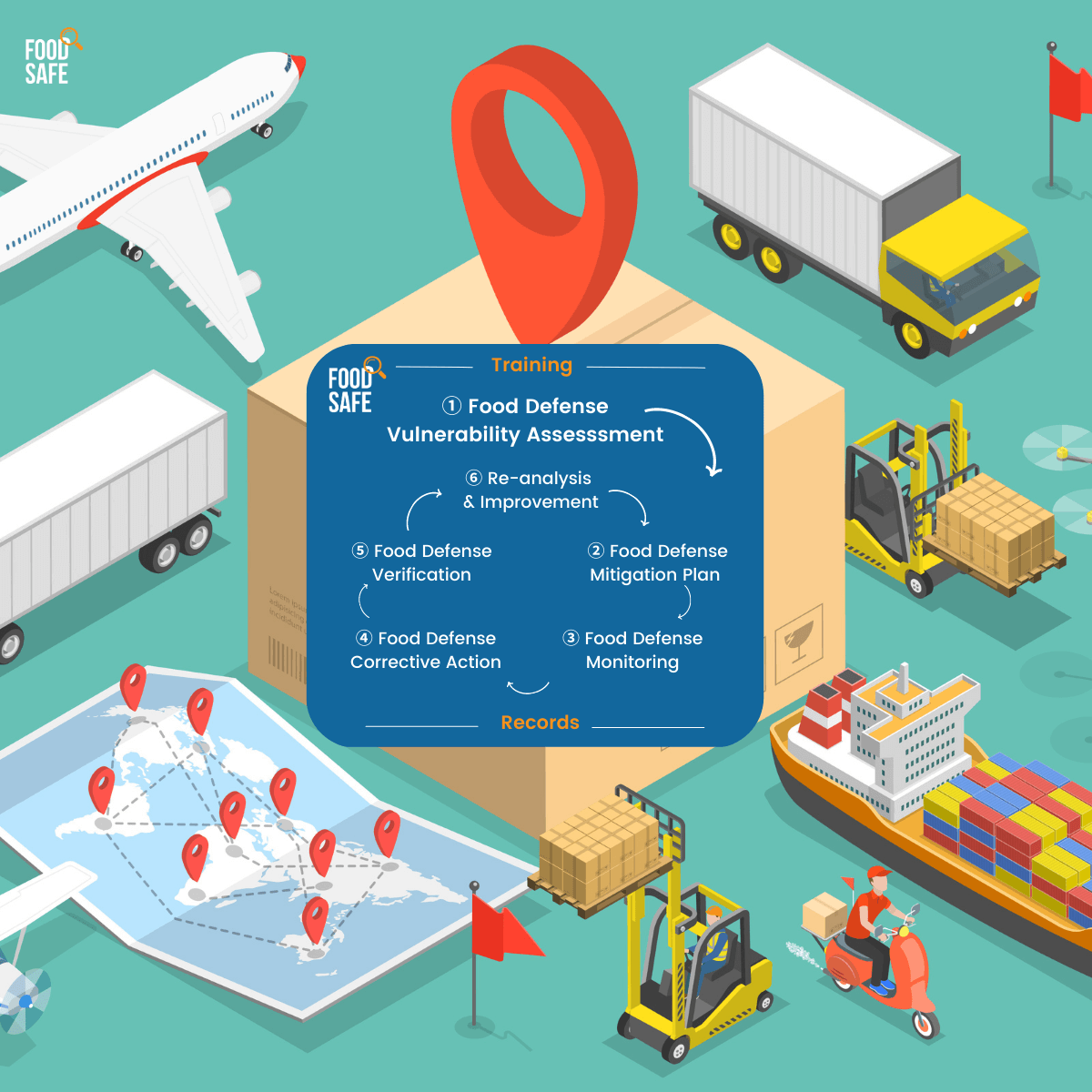
- Vulnerability risk assessment approaches including an introduction to a simple risk matrix, SSAFE, and FDA CARVER+Shock Primer methodologies
- Risk mitigation strategies
- Food Defense Monitoring
- Food Defense Corrective Action
- Defense Verification
- Reanalysis & continuous improvement
- Food defense training and record keeping
- Process steps risk evaluation
- Raw material risk assessment
- Purchasing
- Inwards goods
- Storage
- Production/processing
- Packing
- Dispatch
- Distribution & Logistics
- Best-practice template plan builder, and checklists
- Practical review of your company’s food defense plans
- External audit requirements for food defense penetration test best practice
All this is packaged in a fun and interactive way (don’t take just our word for it, read what our learners for over a decade have to say, by clicking on this link).
Your lead-trainer
- Food Safe’s Food Defense Training Courses are delivered by Food Safe’s Managing Director, Lead-trainer & Food Safety Expert, Keith Michael who holds:
-
- A Masters Degree in Operations Management
- 30+ Years experience in Food Processing & Auditing
- 15+ Years in High-compliance manufacture eg. Infant Formula & RMPs
- Technical Food Processing, Food Safety, and Audit Competencies
- Dairy Manufacturing: Technical & Specialised Operations
- Certificate in Company Direction from the Institute of Directors (IOD), New Zealand
Keith has presented papers at the Food Safety Conferences in 2019, 2020, 2021 & 2022 and brings this cross-sector learning into training.
Keith has over a decade of experience as a company director where he has assisted companies across the globe with Food Safety Compliance, Risk Audit, and closing of gaps identified with smart purpose-built competency training. View Keith’s profile on LinkedIn.
-

About Food Safe
Food Safe Ltd is Accredited by the New Zealand Government + is a Category 1 NZQA-Registered PTE. Training complies with the Food Safety Bylaws and Verifier Audits right across New Zealand.
Our training is trusted by both well known New Zealand and Global food companies and heaps of small teams too! Our training is science-based on New Zealand regulatory and globally recognised best practice – MPI, FAO, FDA, EU
Food Safe’s advisory committee includes leading experts, quality and compliance managers, and governance experts. For even more information about Food Safe and the companies we work with, click here
Why Choose us for your Training?
- Complements compliance audit requirements by NZQA, Category 1 PTE, New Zealand’s highest training provider standard
- Is simplified and visual, and supportive of implementing learning back on-job
- Is delivered by a trained ISO 9001 & 22000 lead auditor
- It is delivered by a trainer with first-hand knowledge and experience in high-compliance operations where Food Safe also operates, such as the meat, dairy, and seafood sector. This allows us to transfer best practices.

120
427
100
How Food Safe collaborates with food companies to deliver food safety training
HOW IT WORKS
FAQs
What is Food Defense?
Food Defense is the effort to protect food from acts of intentional adulteration or tampering. Source: FDA
What is Food Integrity?
The status of a food product where it is authentic and not altered or modified with respect to expected characteristics including, safety, quality, and nutrition. Source: FAO
What is Food Authenticity?
Food authenticity is the quality of a food to be genuine and undisputed in its nature, origin, identity, and claims, and to meet expected properties. Source: FAO
What is Food Fraud?
Any deliberate action of businesses or individuals to deceive others in regards to the integrity of food to gain undue advantage. Types of food fraud include but not limited to: adulteration, substitution, dilution, tampering, simulation, counterfeiting, and misrepresentation. Source: FAO
What is Food Fraud as defined by GFSI and FSSC 22000?
Food Fraud is the collective term encompassing the intentional substitution, addition, tampering, or misrepresentation of food/feed, food/feed ingredients or food/feed packaging, labeling, product information, or false or misleading statements made about a product for economic gain that could impact consumer health (GFSI BRv7:2017). Source: GFSI
What is GFSI?
GFSI stands for Global Food Safety Initiative. (GFSI; the Coalition) is a Coalition of Action from The Consumer Goods Forum (CGF), bringing together 45 retailers and manufacturers from across the CGF membership and an extended food safety community to oversee food safety standards for businesses and help provide access to safe food for people everywhere. Source: GFSI
What is Economically Motivated Adulteration (EMA)?
Economically motivated adulteration (EMA) is a subset of food fraud. It is the intentional substitution or addition of a substance in a product for the purpose of increasing the apparent value of the product or reducing the cost of its production, for economic gain. Source: FAO
What is a Food Safety Management System or FSMS?
A Food Safety Management System or FSMS is a systematic approach to controlling hazards within a food business and supply chain in order to ensure that all food and packaging is safe and fit for purpose. All businesses are required to put in place, implement and maintain a FSMS based on total quality management and the principles of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) with the methodology used to also proactively control vulnerabilities [Vulnerability Assessment Critical Control Point (VACCP)] and threats [Threat Assessment Critical Control Point (TACCP)] Source: Bristol.Gov.UK
What is VACCP?
VACCP is the acronym for Vulnerability Assessment and Critical Control Points. The assessment, analysis and mitigation strategies
is on prevention of intentional adulteration for financial gain in the supply chain. For example: Honey adulterated with sucrose syrup for monetary gain.
What is TACCP?
TACCP is the acronym for Threat Assessment and Critical Control Points. The assessment, analysis and mitigation strategies is on prevention of intentional contamination for ideological and behavioral reasons in the food supply chain. For example: A threat to poison food.
What is Food Dilution?
The process of mixing a liquid ingredient with a high value with a liquid of a lower value. For example, watered-down products using non-potable / unsafe water or olive oil diluted with cheaper oil. Type of risk? Adulterant- substance (Adulterant) Source: FSSC 22000
What is Food Substitution?
The process of replacing an ingredient or part of a product of high value with another ingredient or part of a product of lower value. For example, Sunflower oil is partially substituted with mineral oil. Type of risk? Adulterant- substance or tampering. Source: FSSC 22000
Food Defense Resources
FSSC Food Defense Guidance Document – Source FSSC 22000
FSSC Food Defense Overview– Source FSSC 22000
Food Fraud Vulnerability – Source: SSAFE
Introduction: SSAFE Assessment tool
Strategies to Protect Food Against Intentional Adulteration – FDA
CARVER Plus SHOCK Method for Vulnerability Assessment – FDA
Employees FIRST Video – FDA
Front line employees training
Risk management ISO 31000 – ISO
A Risk Practitioners Guide – Source IRM
Companies we work with
































